An alcoholic who dies is a dead alcoholic. Why should he be anything else? Judging from dream life, the state of consciousness that you have created while you are alive is what you will inhabit after you die, if you are aware at all. This recognition has powerful implications for our understanding of lucid dreams. Just because you wake up in a dream and recognize that you are dreaming does not mean that you are any more spiritual. Alcoholics, criminals, and children can lucid dream. Does that make them more spiritual? The problem arises when people confuse an aptitude, like lucid dreaming, clairvoyance, or psychic healing, with a level of development. It’s like assuming that Einstein is an expert at opera, politics, or love because he is a genius at math.
When you become lucid while you are dreaming you remain locked within the level of development of your waking self. If you are an alcoholic when you are awake, you are an alcoholic in your dreams; if you are an addict to drama in your waking life, you will be addicted to drama in your dreams. Therefore, knowing whether you know you are dreaming or not while you are asleep and dreaming is not so important.
The type of dream yoga taught by Integral Deep Listening teaches that what is important is that you learn to be more awake in whatever state you are in at the moment. When you are asleep and dreaming, your first goal is to recognize drama and to choose not to play. Why? Because if you are addicted to drama and become lucid, you will create drama in your lucid dreams. You will seek out rescuers in the form of Great Teachers, fabulous lovers, or beautiful destinations. You will rescue yourself from perceived threats, such as monsters and fires, thereby implying that you have given them the ability to turn you into a victim. In the process of saving yourself from feared victimization, you will see those same monsters and fires as persecutors, thereby putting yourself in conflict within lucid dreams with the parts of yourself that they represent. Is that smart? Do you want to spend your life creating imaginary conflicts within yourself, conflicts that you will then project onto your friends and the world in an attempt to recognize them and heal them? If an alcoholic who dies is a dead alcoholic, then if you are addicted to drama and become lucid in a dream, you are still addicted to drama.
Tom, who had been addicted to drama, in the form of chronic fear and nightmares, for as long as he could remember, told the following dream: “I was with my friend Johnny and two girls. We were in a cellar. There was a man that at first I didn’t think was a threat, but we were in a trap. The man shouted that he would come down into the cellar and get us. He hit the steps with something heavy, but Johnny wasn’t scared; the girls and I were scared. The cellar was the same as my grandmother’s cellar – my father’s mother.”
This was a lasting replay of a real life memory. When he was four, seven, and sixteen he was forced to sleep in his grandmother’s cellar, all alone. He found it extremely frightening. When he imagined he was both the Cellar and the menacing Man in the dream, and answered questions from their perspective, as one is taught to do with Integral Deep Listening, they reminded Tom of his father, who always wanted to be powerful and in control. In this dream, Tom created persecutors, in the form of the Cellar and the menacing Man. He, Johnny, and the two girls are victims. As in all nightmares, there is no rescuer to be seen. In really good nightmares, people and places that are thought to be rescuers turn out to be persecutors.
By becoming the Cellar and the menacing Man, Tom could recognize that he was scaring himself in the dream. It was his job to do so; he didn’t want to hurt anyone, he just wanted to scare them so that he could feel powerful and in control. In this way he could keep himself paralyzed and “safe,” “trapped in the cellar. However, when Tom became his friend Johnny, the drama changed. Johnny saw that the menacing man was not violent, only scary, and he also saw that he could ignore the man and walk up the steps, out of the cellar and go surfing.
The metaphor here is that you can spend your life locked in the cellar of your own fears, manufacturing threatening people and situations to keep yourself stuck, or you can “wake up” and realize that this is a self-created drama, and spend your life “surfing” instead. The choice is yours; no one makes you stay stuck in your own particular version of Tom’s cellar or Plato’s cave, scared of yourself, scared of others, scared of change, and scared of growing.
When Tom “woke up” to the self-created and optional nature of the drama he was creating in his life, his nightmares became less frequent and then went away. Why? Because his dramas were no longer experienced as “real.” Like a scary movie that has been seen so many times that it becomes both boring and funny, his dreams no longer had the power of genuine threats, once Tom learned to look at his dreams from the perspective of Johnny and recognize that he had a choice whether to be scared and stay scared, or whether to just walk up the stairs and, like the prisoner in Plato’s cave, walk out into the sunlight.
This recognition is not natural; it has to be taught; it has to be learned. Understanding the principle is not enough; the choice of freedom from genuine personal imprisonment must be personally experienced. Therefore, doing Integral Deep Listening interviews is particularly important for the children that you know, because when one learns at an early age how to recognize the self-created dramas within dreams and wake up out of them, they stop incubating fear and victimization every night in their dreams. When they stop, they wake up in a better mood; they have more clarity and confidence in facing the challenges of the day; they have broken the cycle of enmeshment in self-created misery. How might the arc of your own life have been different if you, like Tom, had received such awarenesses as a youth and awakened out of your own delusions?
Such self-created suffering is the real karma of life; it is what hell is all about. Similarly, the self-generated wakefulness that Tom created for himself is the real salvation within life; this is what heaven is all about: learning to live every day surfing the waves of your live instead of choosing to stay locked in a cellar of your own creation.
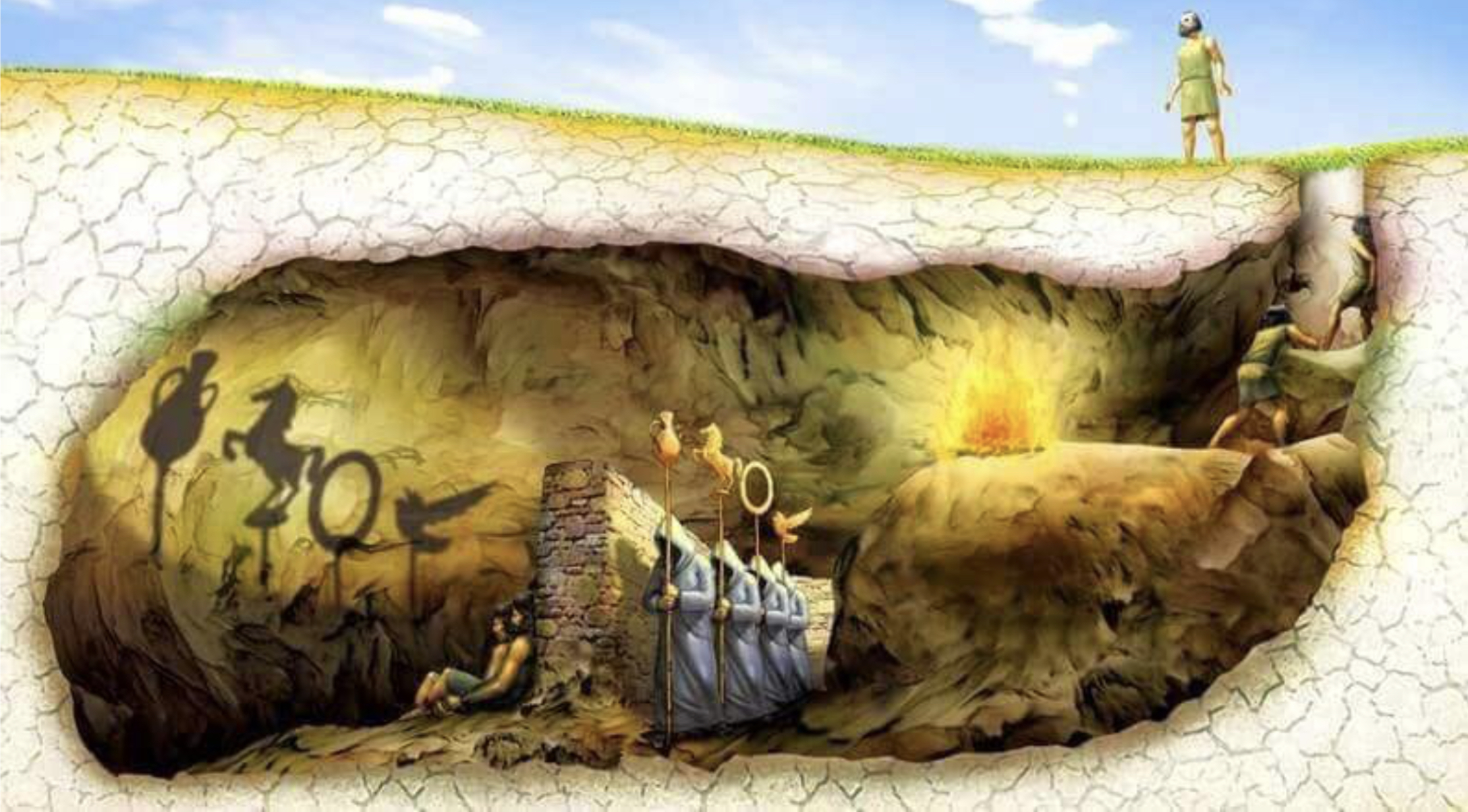
For those of you who wish to delve deeper, here is Plato’s famous myth of the cave:
“[Socrates] And now, I said, let me show in a figure how far our nature is enlightened or unenlightened: –Behold! human beings living in a underground cave, which has a mouth open towards the light and reaching all along the cave; here they have been from their childhood, and have their legs and necks chained so that they cannot move, and can only see before them, being prevented by the chains from turning round their heads. Above and behind them a fire is blazing at a distance, and between the fire and the prisoners there is a raised way; and you will see, if you look, a low wall built along the way, like the screen which marionette players have in front of them, over which they show the puppets.
[Glaucon] I see.
[Socrates] And do you see, I said, men passing along the wall carrying all sorts of vessels, and statues and figures of animals made of wood and stone and various materials, which appear over the wall? Some of them are talking, others silent.
[Glaucon] You have shown me a strange image, and they are strange prisoners.
[Socrates] Like ourselves, I replied; and they see only their own shadows, or the shadows of one another, which the fire throws on the opposite wall of the cave?
[Glaucon] True, he said; how could they see anything but the shadows if they were never allowed to move their heads?
[Socrates] And of the objects which are being carried in like manner they would only see the shadows?
[Glaucon] Yes, he said.
[Socrates] And if they were able to converse with one another, would they not suppose that they were naming what was actually before them?
[Glaucon] Very true.
[Socrates] And suppose further that the prison had an echo which came from the other side, would they not be sure to fancy when one of the passers-by spoke that the voice which they heard came from the passing shadow?
[Glaucon] No question, he replied.
[Socrates] To them, I said, the truth would be literally nothing but the shadows of the images.
[Glaucon] That is certain.
[Socrates] And now look again, and see what will naturally follow if the prisoners are released and disabused of their error. At first, when any of them is liberated and compelled suddenly to stand up and turn his neck round and walk and look towards the light, he will suffer sharp pains; the glare will distress him, and he will be unable to see the realities of which in his former state he had seen the shadows; and then conceive some one saying to him, that what he saw before was an illusion, but that now, when he is approaching nearer to being and his eye is turned towards more real existence, he has a clearer vision, -what will be his reply? And you may further imagine that his instructor is pointing to the objects as they pass and requiring him to name them, -will he not be perplexed? Will he not fancy that the shadows which he formerly saw are truer than the objects which are now shown to him?
[Glaucon] Far truer.
[Socrates] And if he is compelled to look straight at the light, will he not have a pain in his eyes which will make him turn away to take and take in the objects of vision which he can see, and which he will conceive to be in reality clearer than the things which are now being shown to him?
[Glaucon] True, he now.
[Socrates] And suppose once more, that he is reluctantly dragged up a steep and rugged ascent, and held fast until he ‘s forced into the presence of the sun himself, is he not likely to be pained and irritated? When he approaches the light his eyes will be dazzled, and he will not be able to see anything at all of what are now called realities.
[Glaucon] Not all in a moment, he said.
[Socrates] He will require to grow accustomed to the sight of the upper world. And first he will see the shadows best, next the reflections of men and other objects in the water, and then the objects themselves; then he will gaze upon the light of the moon and the stars and the spangled heaven; and he will see the sky and the stars by night better than the sun or the light of the sun by day?
[Glaucon] Certainly.
[Socrates] Last of he will be able to see the sun, and not mere reflections of him in the water, but he will see him in his own proper place, and not in another; and he will contemplate him as he is.
[Glaucon] Certainly.
[Socrates] He will then proceed to argue that this is he who gives the season and the years, and is the guardian of all that is in the visible world, and in a certain way the cause of all things which he and his fellows have been accustomed to behold?
[Glaucon] Clearly, he said, he would first see the sun and then reason about him.
[Socrates] And when he remembered his old habitation, and the wisdom of the cave and his fellow-prisoners, do you not suppose that he would felicitate himself on the change, and pity them?
[Glaucon] Certainly, he would.
[Socrates] And if they were in the habit of conferring honors among themselves on those who were quickest to observe the passing shadows and to remark which of them went before, and which followed after, and which were together; and who were therefore best able to draw conclusions as to the future, do you think that he would care for such honors and glories, or envy the possessors of them? Would he not say with Homer, “Better to be the poor servant of a poor master,” and to endure anything, rather than think as they do and live after their manner?
[Glaucon] Yes, he said, I think that he would rather suffer anything than entertain these false notions and live in this miserable manner.
[Socrates] Imagine once more, I said, such a one coming suddenly out of the sun to be replaced in his old situation; would he not be certain to have his eyes full of darkness?
[Glaucon] To be sure, he said.
[Socrates] And if there were a contest, and he had to compete in measuring the shadows with the prisoners who had never moved out of the cave, while his sight was still weak, and before his eyes had become steady (and the time which would be needed to acquire this new habit of sight might be very considerable) would he not be ridiculous? Men would say of him that up he went and down he came without his eyes; and that it was better not even to think of ascending; and if any one tried to loose another and lead him up to the light, let them only catch the offender, and they would put him to death.
[Glaucon] No question, he said.
[Socrates] This entire allegory, I said, you may now append, dear Glaucon, to the previous argument; the prison-house is the world of sight, the light of the fire is the sun, and you will not misapprehend me if you interpret the journey upwards to be the ascent of the soul into the intellectual world according to my poor belief, which, at your desire, I have expressed whether rightly or wrongly God knows. But, whether true or false, my opinion is that in the world of knowledge the idea of good appears last of all, and is seen only with an effort; and, when seen, is also inferred to be the universal author of all things beautiful and right, parent of light and of the lord of light in this visible world, and the immediate source of reason and truth in the intellectual; and that this is the power upon which he who would act rationally, either in public or private life must have his eye fixed.
[Glaucon] I agree, he said, as far as I am able to understand you.
[Socrates] Moreover, I said, you must not wonder that those who attain to this beatific vision are unwilling to descend to human affairs; for their souls are ever hastening into the upper world where they desire to dwell; which desire of theirs is very natural, if our allegory may be trusted.
[Glaucon] Yes, very natural.
[Socrates] And is there anything surprising in one who passes from divine contemplations to the evil state of man, misbehaving himself in a ridiculous manner; if, while his eyes are blinking and before he has become accustomed to the surrounding darkness, he is compelled to fight in courts of law, or in other places, about the images or the shadows of images of justice, and is endeavoring to meet the conceptions of those who have never yet seen absolute justice?
[Glaucon] Anything but surprising, he replied.
[Socrates] Any one who has common sense will remember that the bewilderments of the eyes are of two kinds, and arise from two causes, either from coming out of the light or from going into the light, which is true of the mind’s eye, quite as much as of the bodily eye; and he who remembers this when he sees any one whose vision is perplexed and weak, will not be too ready to laugh; he will first ask whether that soul of man has come out of the brighter light, and is unable to see because unaccustomed to the dark, or having turned from darkness to the day is dazzled by excess of light. And he will count the one happy in his condition and state of being, and he will pity the other; or, if he have a mind to laugh at the soul which comes from below into the light, there will be more reason in this than in the laugh which greets him who returns from above out of the light into the cave.
[Glaucon] That, he said, is a very just distinction.
[Socrates] But then, if I am right, certain professors of education must be wrong when they say that they can put a knowledge into the soul which was not there before, like sight into blind eyes.
[Glaucon] They undoubtedly say this, he replied.
[Socrates] Whereas, our argument shows that the power and capacity of learning exists in the soul already; and that just as the eye was unable to turn from darkness to light without the whole body, so too the instrument of knowledge can only by the movement of the whole soul be turned from the world of becoming into that of being, and learn by degrees to endure the sight of being, and of the brightest and best of being, or in other words, of the good.”
Plato, The Republic, Benjamin Jowett translation (Vintage, 1991), pp. 253-261
